Time Dilation as a result of Coordinate Transformation
Special Relativity was originally proposed by Albert Einstein in a paper published on 26 September 1905 titled "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies".
All started because of the incompatibility of Newtonian Mechanics with Maxwell's Equations of EM theory. Einstein's developed special relativity, which corrects mechanics to handle situations involving all motions and especially those at a speed close to that of light.
The history of the development of the theory is very interesting but today we are not going to discuss that. Today we are here to understand one of the key feature of STR, which is called Time Dilation. But our way of understanding this will be a bit different and I will only recommend this blog if you have,
A very basic knowledge of Linear Algebra.
A previous exposure to Special Theory of Relativity (STR).
So, let's start our discussion.
A Theory which has so much might...
It creates ideas so bright...
But still it's results block our sight...
Beacuse we can't see what imagination and what reality! right?
–> By Me
A brief introduction to Space-Time Diagrams
A spacetime diagram is a graphical illustration of the properties of space and time in the special theory of relativity.
Spacetime diagrams allow a qualitative understanding of the corresponding phenomena like time dilation and length contraction without mathematical equations. In space-time diagram,
The \(y-\)axis represent \(ct\),i.e., the vertical axis correspond to time.
The \(x-\)axis represent distance along the x axis, as we normally measure distance.
Keeping these points in our mind, we can draw the space-time diagram of some object.
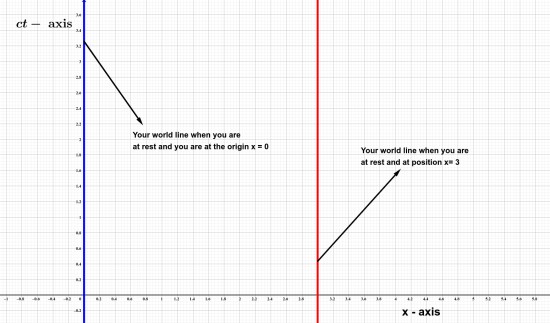
Let's suppose, you are in your room sitting in a chair at rest.
Your position is on changing. You are only going forward in time. So, you will be represented by \(ct-\)axis or a line parallel to \(ct-\)axis depending on your position. As shown in the figure below.
Now, let's see two examples.
Example - 1
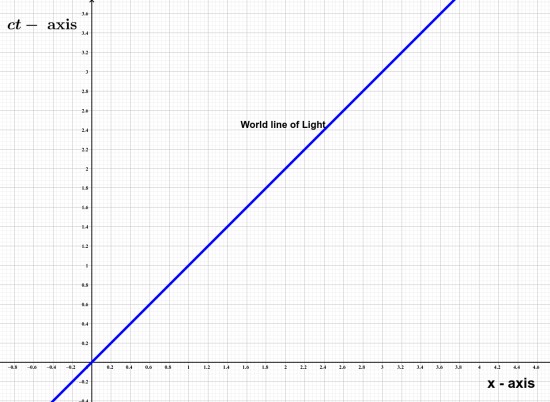
What is the world line of Light?
As, we know the speed of light is constant, which is written as \(c\). Hence, It's equation is,
The axis are represented by \(ct\) and \(x\). Hence, Light's world line will be a line which makes \(45^{\circ}\) angle with the \(x\) and \(ct\) axis and which passes through the origin.
Example-2
Suppose, we have flash running around with a velocity \(0.5c\), i.e., half of the speed of light. What is the world line of flash?
The equation relating flash's path and time is,
The axis are represented by \(ct\) and \(x\). Hence, Flash's world line is a line with slope of \(0.5\), which passes through origin.
Note: Here slope must be measured with respect to \(ct-\) axis.
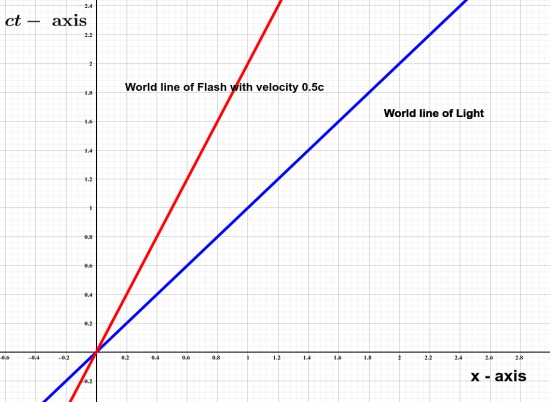
Speed of light is the highest possible speed, as a result any world line must exist above \(x = ct\) line.
To know more about this world line and Space-Time Diagrams watch this amazing series.
Idea of Basis and Space-Time Seperation Vectors
In space-time diagram we have two axis in the plane(Minkowski). As a result (I am leaving the details, we will discuss those in some other blog), we can take two basis vectors along each of those axis.
We will represent the basis vectors by \(\vec{e_x}\) and \(\vec{e_{ct}}\). Keeping these in our mind let's understand Event Vector/Space-Time Seperation Vectors.
Let's suppose, You are a lazy-ass person and you are simply sitting in your room. One of your friend was in that room too, But suddenly he climed on a space ship and started to move with a velocty comparable to the speed of light.
Let's say after moving some distance, he emits a signal. This is represented by the blue point in the diagram below.
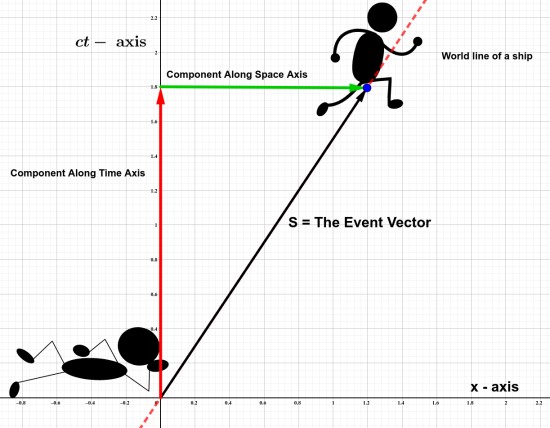
Any event which happens, can be represented by a vector called Space-Time Seperation Vector and can be represented by,
\[ \vec{S} = x_1\vec{e_{ct}} + x_2 \vec{e_x} \]Here, the event1 is the beginning of the motion of your friend and event2 is the instant when he emits the signal.
Let's see another example to make it more clear.
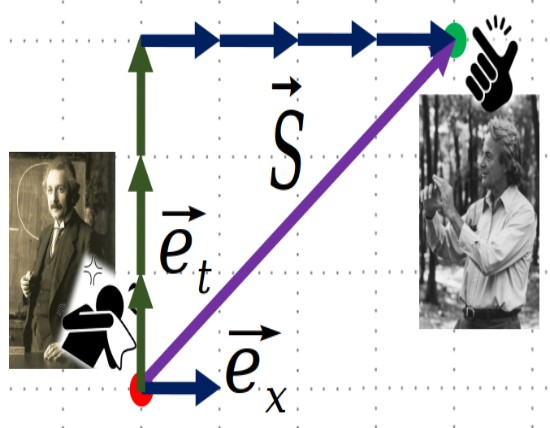
Suppose, Einstein and Feynman both were in a room. When Einstein sneezed, Feynman being the finest man just started to run far from him.
Einstein noticed that after \(3\)sec of his sneeze, Feynman is \(4\)m away from him and at that very moment feynman snapped.
So, Space-Time Seperation Vector for the event1(sneeze) and event2(snap) is,
A Remark on Lorentz Tranaformation and It's effect on basis
I think this blog is already too long and also to discuss Lorentz Transformstion here in it's full glory, It will take huge amount of time. So, I am just going to mention a point here. If you had a course on STR before, then it should make sense. But if it's not clear, then also don't worry. I will discuss this in some later blog.
Suppose, We have two frames,
One at rest.
Another moving with a constant velocty \(v\).
If we want to go from the rest frame to the moving frame, we use Lorentz Transformation. The transformation can be written in terms of matrix,
\[\begin{array}{rcl} T_{LT} = \begin{pmatrix} \gamma & \beta \gamma \\ \beta \gamma & \gamma \\ \end{pmatrix} \end{array}\]where \(\beta = \frac{v}{c}\) and \(\gamma = \frac{1}{\sqrt{1-\beta}}\).
Now, when we go from rest to the moving frame the basis vectors transform. They transform in a way such that they make same angle with the world-line of light and also both the basis vectors tilt inward. It will be clear if someone knows how to visualize linear transformations by looking into the matrix.
I have made one animation which will help you guys understand.  Hope It is clear.
Hope It is clear.
Another Important point which we should always remember is that, when we go to any moving frame, in that frame, the \(ct\) axis lies along it's world line.
Keeping all of these in our mind, we are ready to understand the main topic.
Time Dilation due to transformation of basis
Let's start with the example of Einstein and Feynman. In the Einstein's Frame, he sees that Feynman snaps after \(3s\) of his sneeze.
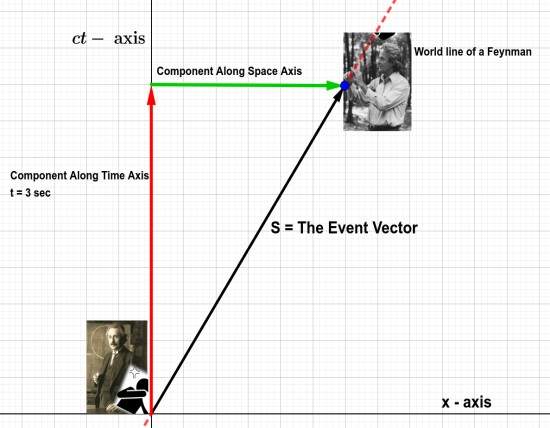
But now what about Feynman's Frame?,i.e., what is the time component of the red arrow in feynman's frame.
To see what happens in his frame, we apply a Lorentz Transformation. The transformation property tells us that Feynman's basis will be a bit tilted as shown.
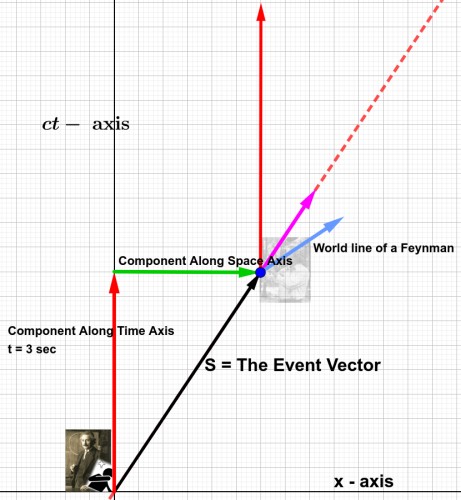
Now, our job is to simply find the component of the time (\(3s\) in einstein's frame) along the pink basis.
Beacuse, the vector is not along the time axis, our intution is already telling us that Einstein will see that in Feynman's moving frame duration has increased. For detail show the image below.
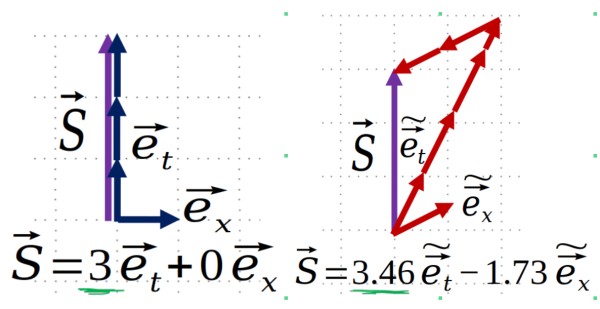
This is how we can intuitively understand Time Dilation using coordinate transformation.
I tried my best to explain this, although I am not sure how much you guys have understood but I hope, atleast you have found of insight on this topic.
A question for you the Reader
Try explaining the Time Dilation using this method for the case of Mueon particle.
If you have some question, do let me know in the comments or contact me using my using the informations are given in the page About Me.
